One of the key tools for data visualization is Power BI, a powerful software platform that allows users to create interactive dashboards and reports. When using Power BI, it is important to choose the right visual for your data, as this will help to effectively communicate the insights you have gleaned from the data.
So, how do you choose the right visual for your data visualization in Power BI? Here are a few key tips:
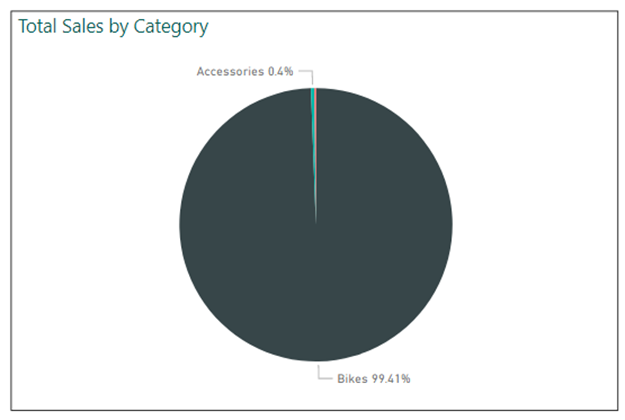
3. Consider the type of data: Different types of data lend themselves to different types of visuals. For example, if you have categorical data (data that can be placed into categories), a bar chart might be a good choice. If you have continuous data (data that can take on any value within a range), a line chart might be more appropriate.
4. Think about your audience: Who will be viewing your data visualization? Is it for a general audience, or for experts in a particular field? The level of understanding of your audience will affect the type of visual you choose.
Here are a few different types of charts available in Power BI, along with the types of data and objectives that they are most suited for:
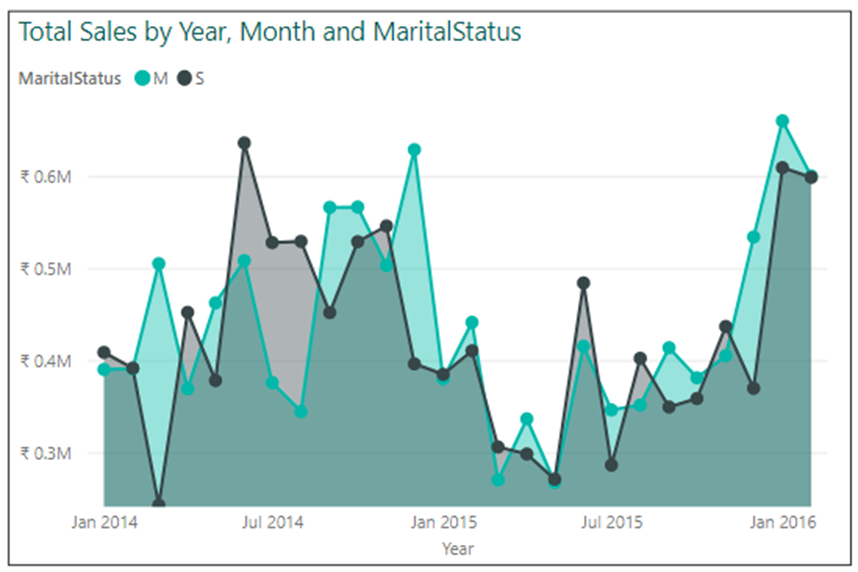
2. Line chart: A line chart is a good visual for showing trends and patterns in continuous data over time. It is especially useful for showing changes in data over a period.
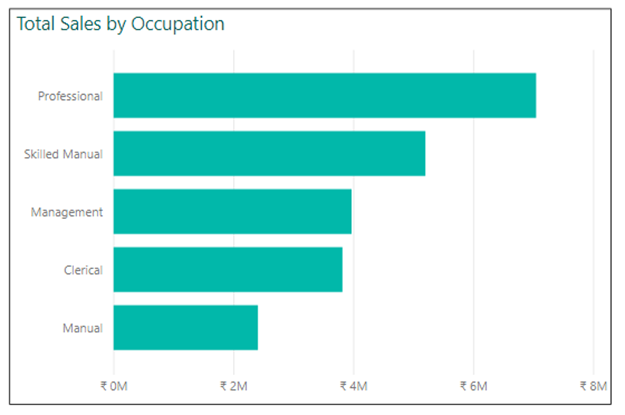
7. Stacked bar chart: A stacked bar chart is a good visual for comparing the proportions of different categories within your data. It is especially useful for comparing values between different categories over time. You can use a 100% stack chart to view the percentage contribution of each country and use sales in tooltips.
- Comparing the sales of different product lines over time
- Displaying the results of a survey or poll, with each data series representing a different response option
- Visualizing the performance of different teams or departments within an organization
- Comparing the performance of different market segments or customer groups.
In conclusion, there are many different types of charts and visuals available in Power BI, each with its own unique features and characteristics. By understanding your data, determining your objective, considering the type of data you have, and thinking about your audience, you can choose the right visual for your data visualization in Power BI.






Comments
Post a Comment